Learning objectives by module
Module 1
Describe strengths and limitations of systematic reviews.
Describe systematic review methods.
Identify different types of systematic reviews.
Identify key components of a systematic review.
Module 2
Describe primary methods of meta-analysis.
Describe purposes of meta-analysis.
Describe strengths and limitations of meta-analysis.
Identify key components of meta-analysis.
Module 3
Describe roles of advisory board members.
Describe the amount of time, level of effort, and resources needed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Explain why systematic reviews require teams.
Identify factors that contribute to the amount of time, level of effort, and resources needed.
Identify guidelines for the conduct and reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
Identify the knowledge and skills required to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Module 4
Describe tasks involved in formulating a problem for a systematic review.
Explain the importance of careful problem formulation in systematic reviews.
Identify characteristics of well-formulated questions for systematic reviews.
Identify different types of questions that can be addressed in systematic reviews.
Identify potential motivations and sources of questions for systematic reviews.
Identify questions that are not appropriate for systematic reviews.
Module 5
Describe purposes of narrow versus broad reviews.
Describe relative advantages and disadvantages of narrow versus broad reviews.
Recognize the importance of issues of scope in planning for systematic reviews.
Recognize the importance of key constructs in systematic reviews.
Module 6
Construct a logic model for a systematic review.
Construct a theory of change for a systematic review.
Describe the uses of logic models and theories of change in systematic reviews.
Module 7
Define the components of PICOS eligibility criteria.
Describe uses of eligibility criteria in systematic reviews.
Develop a well-formulated question and specify relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Identify other potential eligibility criteria.
Module 8
Describe the contents of a protocol.
Describe the purposes of protocols for systematic reviews.
Describe the rationale for public registration of protocols.
Module 9
Explain how to work with an information specialist on a systematic review.
Module 10
Generate a list of scholarly databases to search that aims to achieve thorough coverage for your systematic review research question(s).
Module 11
Compare and contrast systematic review searching with traditional literature review searching.
Construct an effective concept-blocked search strategy correctly using various search elements such as subject headings, keywords and operators.
Explain how and when to use search filters, limits and hedges in a systematic review search.
Use database syntax and field searching appropriately in the design of a systematic review search strategy.
Module 12
Translate the different elements of a search from one database to another using the correct database syntax.
Module 13
Design and document a search process for grey literature sources for a systematic review.
Module 14
Use a variety of supplementary searching methods to identify additional studies related to your systematic review not found through database and grey literature searching.
Module 15
Document and report your search methods for reproducibility and transparency.
Run searches making use of database features for saving and exporting search results.
Use a citation manager to import search results and deduplicate across different sources.
Module 16
Describe the goal of the screening process.
Describe the screening process.
Module 17
Identify best practices for screening questions.
Module 18
Describe the process for training screeners.
Module 19
Describe how multiple reports on the same sample can benefit a systematic review.
Describe the screening process.
Module 20
Demonstrate understanding of percentage agreement and kappa
Identify the information that will need to be reported about the screening process.
Module 21
Describe the screening process.
Module 22
Describe purposes of data extraction and coding.
Describe steps in the process of data extraction and coding.
Module 23
Describe the rationale for linking studies and reports.
Describe the types of bibliographic information that should be extracted from included studies.
Identify intervention characteristics for data extraction (if applicable).
Identify sample characteristics that can be extracted from included studies.
Identify the types of data that need to be extracted in order to describe the methods of included studies.
Identify types of data to extract on study results.
Module 24
Describe essential principles of data extraction and coding in systematic reviews.
Describe the process for pilot testing data extraction forms.
Describe the process for training coders.
Describe the purpose and methods of reliability checks on data extraction and coding.
Describe the purposes of pilot testing.
Describe the purposes of training for coders.
Describe the rationale for using structured data extraction forms.
Describe three ways to structure data extraction forms.
Module 25
Describe diverse approaches to critical appraisal in systematic reviews.
Describe the purposes of critical appraisal in systematic reviews.
Identify key features of critical appraisal in systematic reviews.
Identify potential topics for critical appraisal.
Identify steps in selecting, adapting, and testing critical appraisal methods.
Module 26
Articulate common sources of dependent effect sizes in meta-analysis.
Describe the contents and uses of a flat file.
Identify steps for handling missing data in the extraction and coding process.
Module 27
Identify information that should be reported to describe included studies.
Identify information that should be reported to describe the coding process.
Identify two ways to report results of critical appraisal.
Module 28
Assess differences in systematic review software to choose the best option for your systematic review team.
Module 29
Articulate what standardized effect sizes are
Define effect size.
Demonstrate understanding of what probability values mean
Module 30
Demonstrate understanding of the correlation family of effect sizes
Demonstrate understanding of the mean difference family of effect sizes
Demonstrate understanding of the odds ratio family of effect sizes
Demonstrate understanding of the role of effect size variance and standard error in meta-analysis.
Module 31
Demonstrate understanding of how to read a forest plot.
Demonstrate understanding of what vote counting is
Module 32
Demonstrate understanding of how a simple meta-analysis is conducted
Demonstrate understanding of how effect size confidence intervals, precision, and weights are related
Demonstrate understanding of the general concept behind weighting
Module 33
Demonstrate an understanding of effect size heterogeneity
Demonstrate understanding of how to compute the homogeneity test
Module 34
Demonstrate an understanding of metrics used to describe heterogeneity
Demonstrate understanding of the considerations for choosing the meta-analytic model.
Describe how model choice affects the statistics arising from a meta-analysis
Module 35
Articulate benefits and challenges of using meta-regression to explore heterogeneity.
Demonstrate an understanding of challenges to interpreting moderator analyses.
Demonstrate understanding that exploring effect size heterogeneity requires careful planning in early stages of the systematic review.
Module 36
Demonstrate understanding of publication bias
Demonstrate understanding of the elements of a funnel plot
Module 37
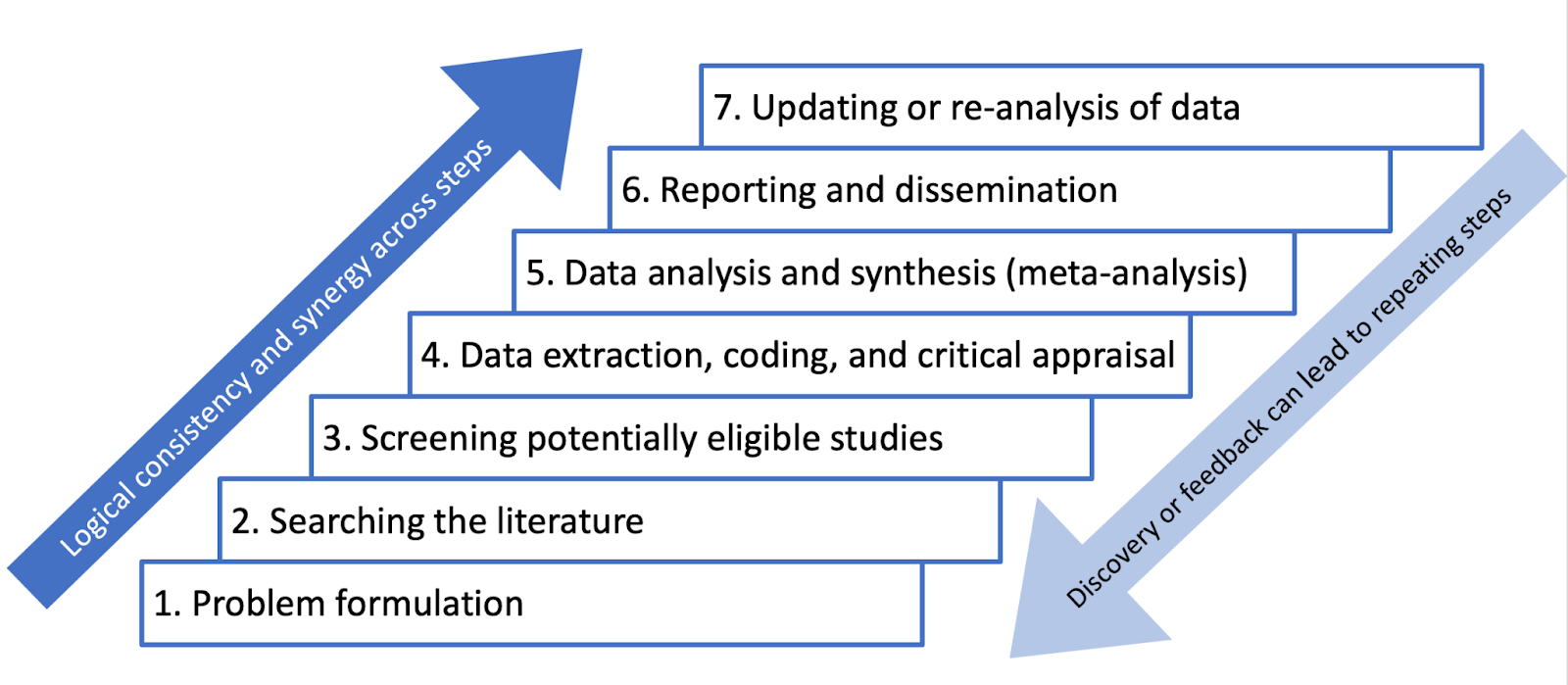
Demonstrate understanding of iterative steps in the systematic review process.
Describe different products of systematic reviews for different audiences.
Describe the importance of logical consistency throughout a review.
Identify guidelines for the conduct and reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
Identify key components of a systematic review.
Identify key components of meta-analysis.
Identify reasons for updating and/or re-analysis of data in systematic reviews.
Module 38
Access resources for learning more about different review methods.
Describe some common review methods beyond systematic reviews.
Identify advanced meta-analytic methods.
Module 39
Access information about tools and platforms that can facilitate systematic reviews through automation.
Access resources for learning more about living systematic reviews.
Describe living systematic reviews.
Describe some steps of evidence synthesis in which automation may be applied.
Describe uses of data repositories.
Explain the role of automation in the evidence synthesis process.
Module 40
Describe the importance of systematic reviews and meta-analysis
Identify resources for learning about advancements in methods for systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
Course assessments, activities, and outline
UNIT 1: Introduction
Module 1: Systematic reviews
Module 2: Meta-analysis
Module 3: What to expect
UNIT 2: Problem formulation
Module 4: Posing answerable questions
Module 5: Setting the scope
Module 6: Using logic models and theories of change
Module 7: PICOS inclusion and exclusion criteria
Module 8: Developing a protocol
UNIT 3: Searching the Literature
Module 9: Working with an information specialist
Module 10: Identifying sources to search
Module 11: Designing Database Searches
Module 12: Translating searches across databases
Module 13: Searching the grey literature
Module 14: Supplementary searching
Module 15: Running, documenting and reporting searches
UNIT 4: Screening Potentially Eligible Studies
Module 16: Introduction to screening potentially eligible studies
Module 17: Creating a screening guide
Module 18: Training screeners and pilot testing the screening process
Module 19: Full-text screening
Module 20: Reporting standards for the screening process
Module 21: Screening potentially eligible studies unit summary
UNIT 5: Data Extraction and Coding
Module 22: Introduction to data extraction and coding
Module 23: Types of data to extract and code
Module 24: Methods of data extraction and coding
Module 25: Structured critical appraisal
Module 26: Preparing data for analysis and synthesis
Module 27: Reporting the coding process and results
Module 28: Software support
UNIT 6: Introduction to Effect Sizes
Module 29: General introduction to effect sizes
Module 30: Three families of effect sizes
UNIT 7: Introduction to Meta-Analysis
Module 31: Introduction to meta-analysis
Module 32: Meta-analysis
Module 33: Homogeneity part 1
Module 34: Homogeneity part 2
Module 35: Exploring heterogeneity
Module 36: Introduction to publication bias
UNIT 8: Course Wrap-up
Module 37: Summary of systematic review and meta-analytic methods
Module 38: Other evidence synthesis methods
Module 39: Technological advances to improve efficiency
Module 40: Conclusions